Table of Content
TABLE OF CONTENTS

This blog post section gives an overview of GDPR, requirements, impact on business, common challenges faced by organizations and next steps recommended for GDPR compliance.
GDPR –Overview
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), enacted in April 2016 in Europe, will come into effect globally on May 25, 2018. The objective of GDPR is to provide a cohesive privacy law for companies and increased data protection for EU citizens (Subjects). GDPR regulates how EU residents’ personal data is collected, processed, stored, deleted, transferred and used by organizations irrespective of their physical location.

The regulation applies if the information/data controller (an association that gathers information from EU occupants) or processor (an association that procedures information in the interest of information controller e.g. cloud service providers) or the information/data subject (person) is situated in the EU.
As indicated by the European Commission "individual information is any data identifying with an individual, regardless of whether it identifies with his or her private, professional or public life. It can be anything from a name, a place of residence, a photograph, an email address, bank details, and posts on social channels, therapeutic data, or a PC's IP address.
It is mandatory for organizations to comply with the new data protection principles and failure to do so could lead to warnings followed by fines. The maximum fines are the greater of 20 million euros or 4% of the company’s worldwide revenue.
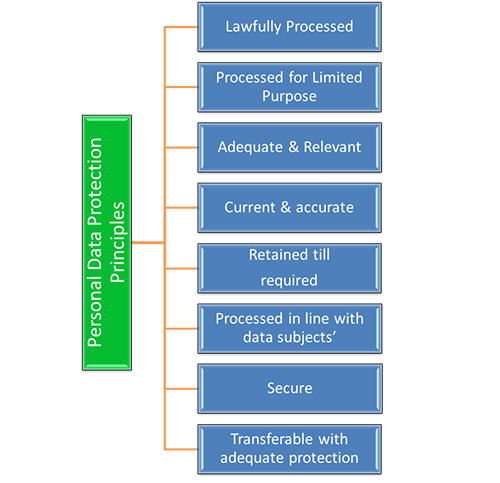
Figure 1: New Data Protection Principles
GDPR Requirements and Impact
Requirements
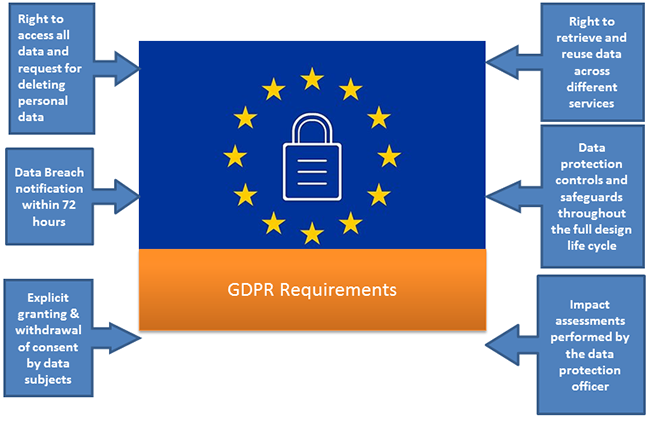 Figure 2: GDPR Requirements
Figure 2: GDPR Requirements
Consent
Consent conditions are strengthened and requirements are more stringent. Data Subjects should be clearly informed on why the data is required and how will it be used. Consent must be granted explicitly and withdrawn at any time by the Data Subjects. While obtaining consent for data use, companies have to explain the terms and conditions in simple terms avoiding legalese.
Breach notification
Breach notification is to data subjects and to supervisory authorities, within 72 hours of Breach identification. In the event of a data breach, data processors have to notify their controllers and data subjects of any risk within 72 hours.
Right to access
Right to access applies to associated personal data, actions and reports. Data subjects will have the right to access free of charge, all data collected and to obtain confirmation of how it is being processed
Right to be forgotten
Right to be forgotten includes erasing personal data and halting personal data processing. This enhances data control throughout its lifecycle. Organizations cannot hold data for any longer than necessary. Likewise, they cannot change the use of data from the purpose for which it was originally collected. Data should be deleted at the request of the data subjects.
Data Portability
Data portability allows data subjects to be provided with their personal data upon request and in a format that facilitates transmission to another data controller. Data Portability also allows data subjects the right to retrieve and reuse personal data for own purposes across different services
Privacy by Design
Privacy by design includes data protection controls and safeguards throughout the full design life cycle of systems, applications and other processes. Inclusion of Data protection is applicable from the onset of designing systems, implementing appropriate technical and infrastructural measures
Formally assigned data protection officers perform internal recordkeeping requirements.
Data Protection Impacts Assessments
Data protection impact assessments must be performed by the data protection officer. They will be engaged in systematic monitoring or processing of sensitive personal data.
Business Impact
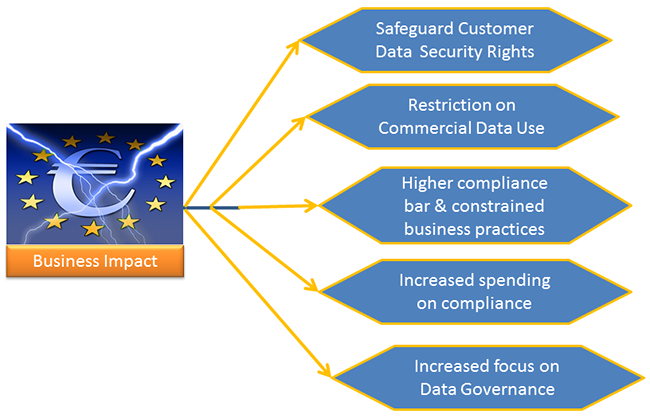
Figure 3: Impact on Business
- Safeguard Customer Data Security rights
- Restriction on commercial data use
- Higher Compliance bar and more constrained business practices
- Increased Spending on Compliance Efforts
- Increased focus on data governance will accelerate digital transformation
Common Challenges
- Data has to be identifiable, auditable, and accessible on request. The way an organization collects, stores and processes personal information has to be modified if necessary in accordance with the new data privacy rights.
- Unstructured data will pose a great challenge because it is difficult to obtain full information from the data.
- Streamline operations, eradicating unnecessary data collection and limiting processing to data which is essential to the core business goals.
- Data Security should be an integral part of all systems from the outset rather than applying in retrospect. One of the greatest challenges would be legacy systems where network-level security has to be in place as the first layer of defense, until the legacy systems introduce new data management modules to implement policy.
- Technological changes in the digital economy and the associated cyber threats call for continuous risk assessment and updating of compliance measures. When new vulnerabilities are discovered, the data protection practices that are considered compliant today may have to be updated to remain compliant in future
GDPR Readiness – What should your business do now
- Enterprises have to take a holistic view of IT Security, data security and information management to accelerate their digital business
- Mitigate Risk and drive value with Better Information Control
- Examine their existing capabilities and evaluate, realistically on their fitness
- Access and comprehend human and computer-created data
- Organize and control this data with a centralized policy engine
- Intelligently manage and take action upon this data in accordance with data privacy.
Roadmap to Compliance
The first and foremost step is to identify and audit your data. Once this is done, the roadmap to GDPR compliance will have better clarity. Adhering to a compliance and standards-based framework can help businesses attract and enhance customer retention. An organization has to invest in security, data privacy and customer care.
Controlling the 5W’s of an individual’s personal data, what (data is being collected), why (the purpose for which it was collected), who (has access to the data), where (the source data was captured) and when (the data captured) are mainstays in building trust.
GDPR compliance is a combination of technical requirements, legal analysis, process definition, documentation and human oversight. Hence, organizations should consult with their legal experts on their individual compliance requirements.
How to Bridge the Compliance Gap?
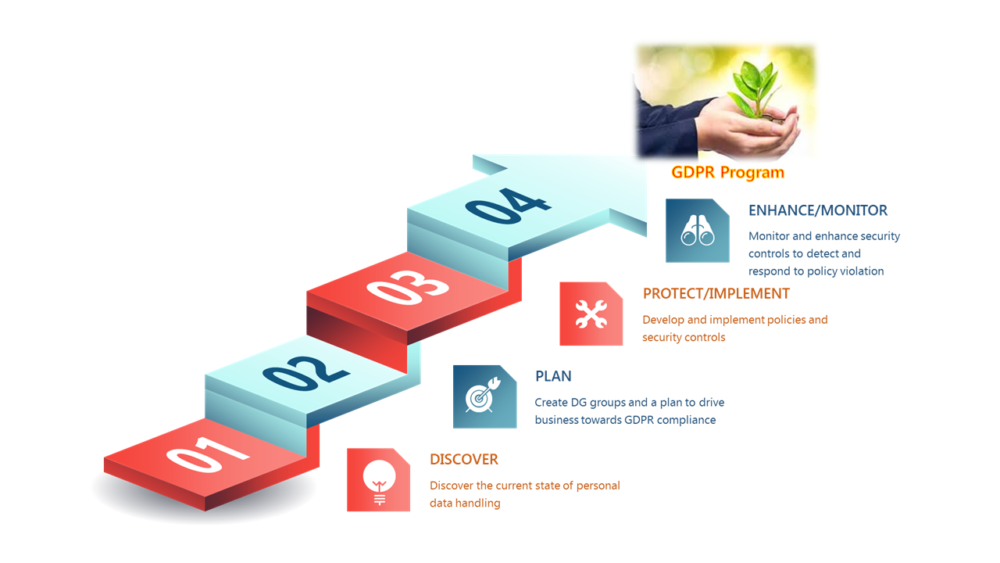
Figure 4: Bridging the Compliance Gap
Discover
Discover the current state of personal data processing in the organization and classify all personal data that an organization collects, processes and stores. Discover the data by looking into every channel, device and location within and beyond an organization’s network, identify and classify structured and unstructured personal data that is captured, processed and stored. Classification will determine the required security controls..
Plan
Create a plan to drive the business towards complete GDPR compliance by bridging all identified gaps, and allotting a budget for technology solution and implementation services. Determine high-risk gaps that require immediate security. A set of data protection and management policies in alignment with the GDPR requirements has to be created by the business. The policies should have a clear definition on personal data access, handling, security, retention, portability and storage within the organization.
In the event of a data breach, organizations have to develop and document an incident response process to identify and respond to any personal data breach, include a data deletion and breach notification process to report the breach within 72 hours.
Protect/Implement
Develop and implement effective security controls to protect all personal data. Organizations have to encrypt and protect all personal data to reduce the likelihood and impact of a data breach.
Business has to elect a Data Protection Officer (DPO) if significant amounts of data are processed on a regular basis. DPOs have to report to the CEO and involved in all compliance regulatory matters. A central compliance team (Data Governance Team) consisting of legal, HR, PR, business unit leads, the DPO, IT and security should review the GDPR program on an ongoing basis to measure full compliance.
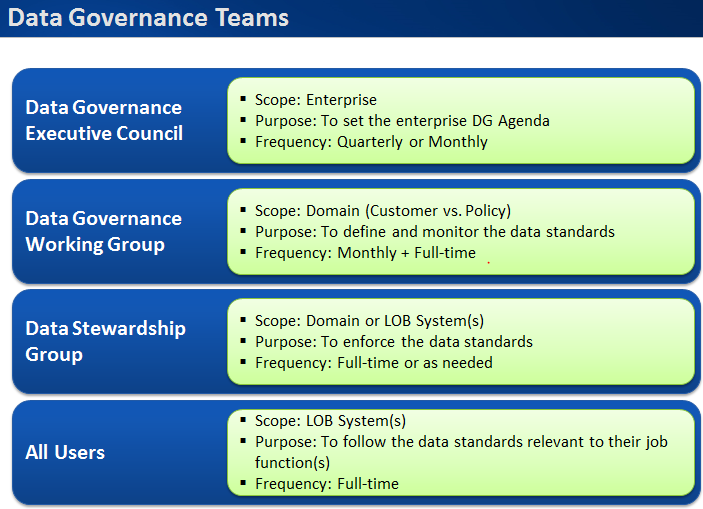
The following diagram clearly explains the role-play of the Data Governance Group team members at each stage, namely the “Initiate stage”, “Define and Optimize Stage”, “Design and Deploy Stage”
Figure 5: Data Governance Group
Enhance/Monitor
Enhance security controls, monitor, detect, respond and report all policy violations and external threats. After deploying controls to fill the identified gaps, continuous monitoring is necessary to measure the effectiveness. Data Protection risks have to be constantly evaluated and the effectiveness of deployed security controls in preventing security breaches have to be estimated. Vendor risk assessment is mandatory. Business has to assess compliance levels of existing and new vendors on an ongoing basis.
Stay tuned for Part2 of this two-part series on addressing GDPR compliance efforts. Please send us a note with your queries and feedback.
Tags
Data-as-an-Asset
Shylaja Rajendran
Senior Architect
Experience of 11 years and has managed complex Enterprise Data Integration & Enterprise Application Integration Projects
-2.jpg?width=240&height=83&name=Menu-Banner%20(5)-2.jpg)
.jpg?width=240&height=83&name=Menu-Banner%20(8).jpg)